Why is sleep so important?
During sleep, the body undergoes various restorative processes, including memory consolidation, hormone regulation, and tissue repair. Adequate and quality sleep is crucial for cognitive function, emotional wellbeing, immune system support, and overall physical health. Insufficient sleep can lead to a range of negative effects, such as impaired concentration, mood disturbances, and increased risk of various health conditions.
Benefits of Good Sleep

Cognitive Function
Sleep is vital for cognitive processes such as memory consolidation, learning, and problem-solving. It enhances creativity, decision-making, and overall mental clarity.

Emotional Wellbeing
Adequate sleep contributes to emotional resilience and stability. It helps regulate mood and stress levels, reducing the likelihood of mood disorders and emotional disturbances.

Physical Health
Sleep is intricately linked to physical health. It promotes the proper functioning of the immune system, supporting the body’s ability to fight off infections and diseases. Chronic sleep deprivation has been associated with an increased risk of various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity.
Hormonal Balance
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating hormone levels, including those responsible for growth, stress response, appetite, and metabolism. Disruptions in sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting overall health.
Cellular Repair & Recovery
During deep sleep, the body undergoes processes of cellular repair and regeneration. This is essential for maintaining healthy skin, muscles, and other tissues, as well as supporting overall physical recovery.

Energy Conservation
Sleep serves as a period of energy conservation, allowing the body and brain to rest and recharge. This ensures optimal performance and alertness during waking hours.

Memory & Learning
Sleep is instrumental in consolidating and organising memories. It plays a crucial role in the transfer of information from short-term to long-term memory, contributing to effective learning and knowledge retention.
Motor Skills
During sleep, the brain consolidates and refines motor skills learned during waking hours. This is essential for activities that involve coordination, precision, and muscle memory. Quality sleep supports the refinement of fine and gross motor skills, contributing to improved physical capabilities.
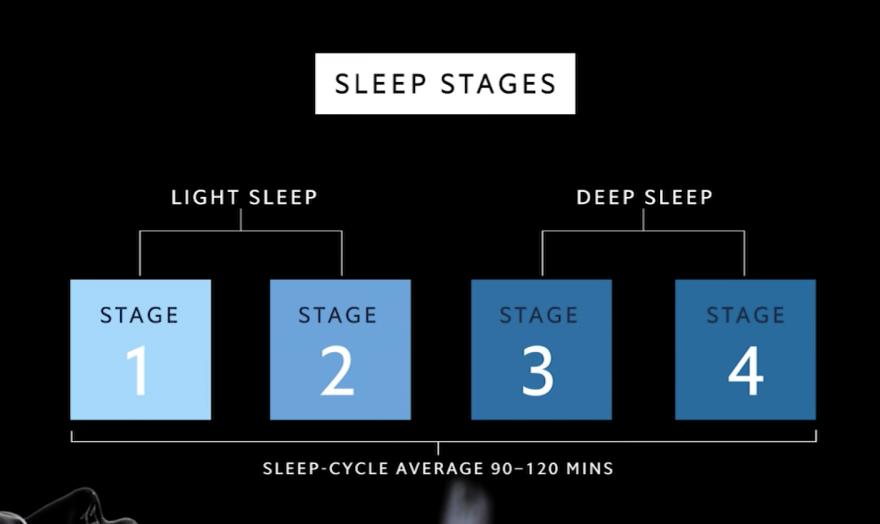
The Stages of Sleep
Ever wondered what happens when you sleep? There are 4 distinct stages of sleep that our bodies experience each night. From the initial moments of drifting into slumber, to the deep and rejuvenating sleep that follows, discover why each stage is essential for a restful night and optimal health.
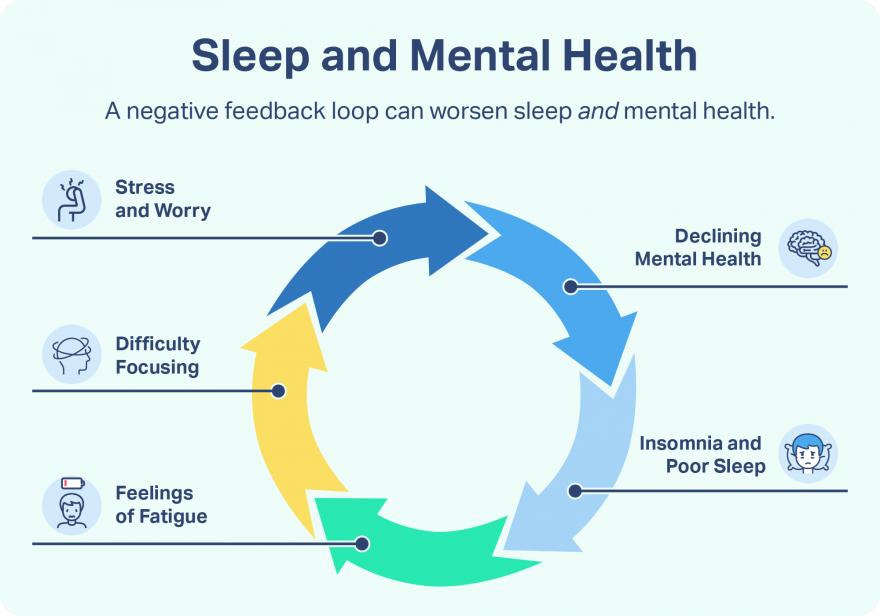
How can sleep affect our mood and mental health?
Sleep has a very close relationship with both our mental and emotional health: poor mental health can affect your sleep and poor sleep can also affect your mental health.
Sleeping allows both our body and our brain to rest, recover and repair so we are ready for the next day. During sleep, our brain is still very much active and will begin to evaluate and process our emotional information. This includes aspects such as our thoughts, our memories and what we might have learnt. A lack of sleep and/ or poor sleep quality is very disruptive and harmful to this important process, and can interfere with the proper consolidation of our emotional processing. As a result, this can have a significant impact in our waking life on aspects such as our mood, memory and other cognitive functioning.
As a consequence, ‘tiredness’ can begin to interfere with both professional and personal life which can lead to increased worry, stress or frustration - all of which can negatively affect sleep, and so a vicious cycle begins to formulate as demonstrated below. If continued for a prolonged period of time, this can lead to an increased risk of poor mental health.
How can I improve my sleep?
We all need sleep, but sometimes we can find it difficult. Implementing some sleep strategies can contribute to a more consistent and restful sleep pattern, promoting overall wellbeing and daytime alertness. Below are 6 practical ideas that can use to help improve your sleep quality and duration and establish better sleep hygiene.
NOTE: Self-help techniques can be helpful when working to establish a more normal sleeping pattern. However, if sleep problems continue, please speak to your GP as struggling to sleep can sometimes be symptoms of other conditions.